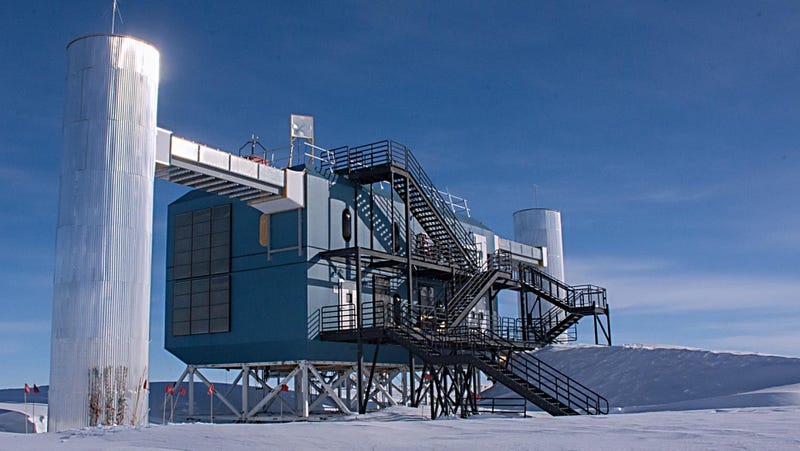

For more than past 20 years scientist are operating this facility in Antarctica at an altitude of 9000 feet and temperatures that never go above -30 degree centigrade. The sun shines so bright here in lack of Ozone layer that you may need sunscreen to protect your nostrils. But what on earth do you get for living in such harsh weather ?
A few days back this place has marked its spot in the history of mankind when it detected Neutrinos from a definite location in sky. Let us look at what are Neutrinos, their detection and the implication to astronomy in future.
Neutrinos !
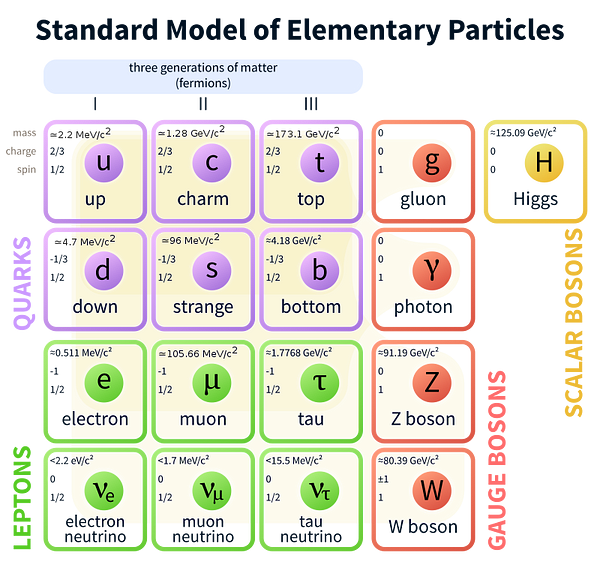
All of us have conveniently learned is school that all the matter we see is made up of atoms, But an atom itself is made of protons, and neutrons in the center of it and electrons in an orbit around it.
There are particles that are more fundamental to these are the ones shown in the diagram. They are the reason of our very existence, one of such particle is a Neutrino.
Neutrinos are released from atoms when they decay through a specific mechanism called the Beta-Decay. Stars, Our own sun, Nuclei of active galaxies, regions in and around black holes and Radioactive materials are some of the key sources that produce these particles.
Neutrinos are one of the most harmless particles you can imagine of. They are almost massless, so much so that their mass was considered to be zero for lot many years after their discovery. As the name suggest they are also chargeless and do not interact with regular matter electrically. These particles are found in abundance in nature. They travel at almost the speed of light.
They are almost Ghost-like, 400 billion Neutrinos pass through your thumbnail each second without you detecting it. They do not interact (collide) with regular matter and pass through it. Most Neutrinos from the sun can pass right through the earth to the other side without any interaction. Detecting such particles is also an immense challenge by itself.
Detecting the Neutrinos
Neutrinos are sneaky little particles and almost impossible to detect directly. The Neutrino is also from Italian meaning Neutral little one. However Many indirect techniques are used to detect them though.
Indirect techniques means detecting presence of neutrinos using the effects it has created in surroundings. To say your friend is not at home when you see that his car is not parked outside his home, is an indirect technique.
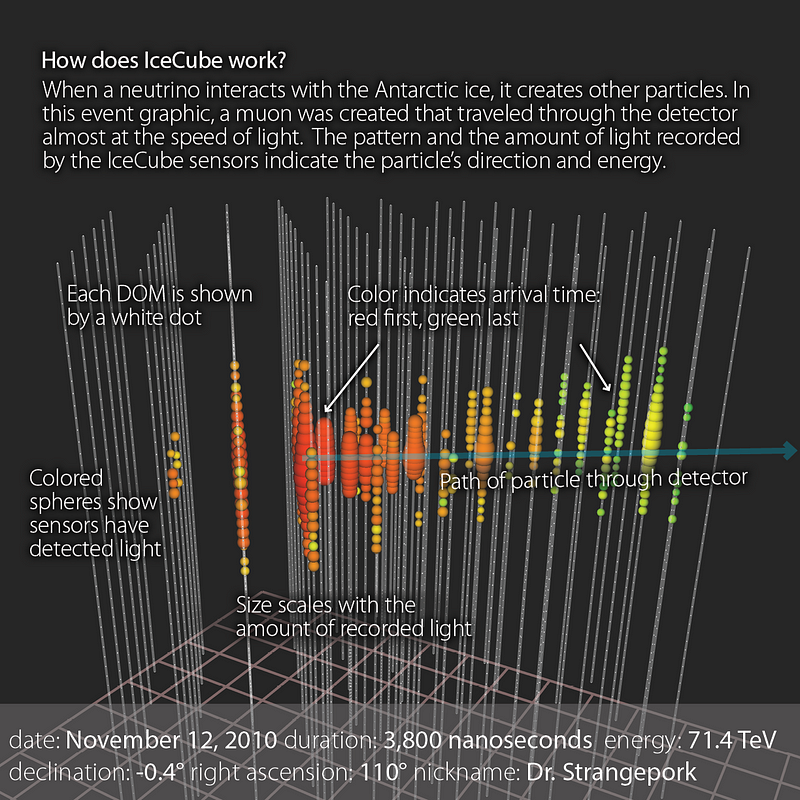
When Neutrinos pass from any material they at times scatter or release radiation in form of light or change the characteristic of the atoms of the material that Neutrino passed from.One of the most dominant detection technique and the one employed at Ice-cube is through cherenkov radiations. These radiations are released by Neutrions when they pass through a material like ice or water. Neutrions can travel faster than light in these materials and this in turn creates Cherenkov radiations. We detect this radiation and predict the existence of Neutrino that has passed.
Ice-Cube Detector
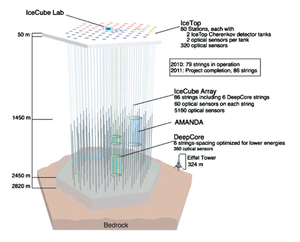
Ice-cube detector is made in the pristine ice of the Antarctica that allowed an unhindered detection using Cherenkov radiations. There are a many detectors called the digital optical modules that are lowered into the ice as deep as 2450 meters. There are some 5,160 such modules that have been placed using 86 strings in the drilled holes of ice. Look at the Eiffle Tower in the image for comparison. Building such instruments in Antarctica is a challenge by itself.
The Ice-cube has the ability to derive many characteristic between the incoming Neutrinos and segregate them depending upon their energies and origin as to whether they are from a cosmic source or not? It can also predict directions of incoming neutrinos in such cases.
Multi-Messenger Astronomy
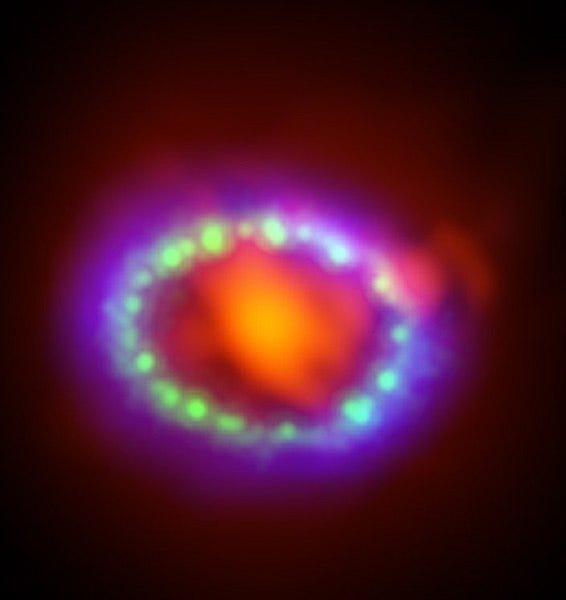
In 1987 the first naked supernova after the advent of the telescope age happen. At the same time the Kamikonde Neutrino detector experiment detected several neutrinos and they were confirmed to have arrived from the same explosion. This was the birth of the Neutrino based astronomy.
Almost 4 decades later the tables have turned and Icecube became the first Neutrino experiment where detection of neutrinos occurred first and the direction of the incoming neutrino was determined. Later an alert was issued to may of the telescopes across the globe and they detected a Blazar at that location. It is as if we had sniffed the presence of the Blazar by just 13 neutrinos. A blazar is a very active blackhole that emits a very energetic stream of energy as it spins.
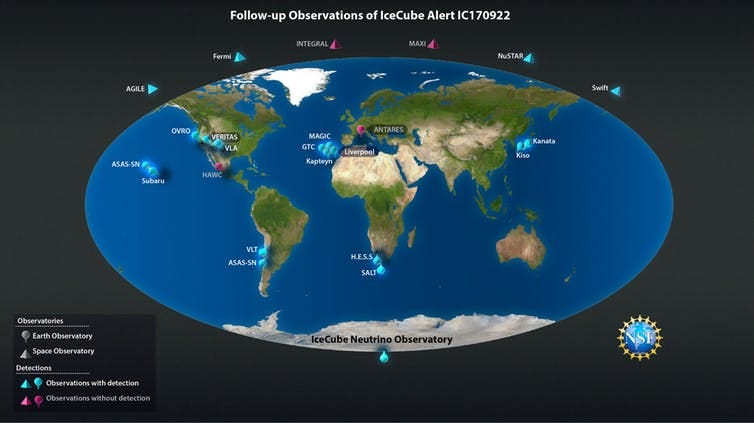
Ground based telescopes, space based telescopes and Neutrino detection made this a very diverse event in itself with multi spectrum observation.
Future Prospects and Multi-Messenger astronomy
First we used to observe the sky only using eyes in the visible spectrum. Then we could observe the same in the sky using the many different light spectra like IR, UV, gamma and X-rays. Then we could detect cosmic events using Gravitational Waves that are a new form of waves. They were attributed as having our ears in space now we could also hear the dynamic noises in the space.
With neutrino based observatories it more like we can sniff out events in space using neutrinos. It is also important to note here that the neutrinos are not waves like the other cases are.
Such detectors add to the endless possibilities to explain dark matter, Cosmic ray bursts and dynamic events in the universe like the supernova explosions, Blazars, Pulsars, Colliding bodies and many more.
With so many sense to observe the outer space universe and mother nature is bound to surprise us in ways previously unimaginable.
Lost opportunity for India ?
Indian scientist have tried to set up a Neutrino observatory in India since the 1990’s. The project has been delayed a several times owing to lack of environmental clearances, ministerial apathy and hoaxes.
Fake news that such projects pose major health risk to villagers nearby has led to strong opposition and added difficulty to the project. While it is clear that Neutrions are the most harmless particles such news spread, for an intention of malice has done much harm.
It is imperative that all of us should take up the job to educate peers about the benefits and harmlessness of such projects and become catalysers to the scientific prog
ress of our country rather than impediments.
Comments
Post a Comment